

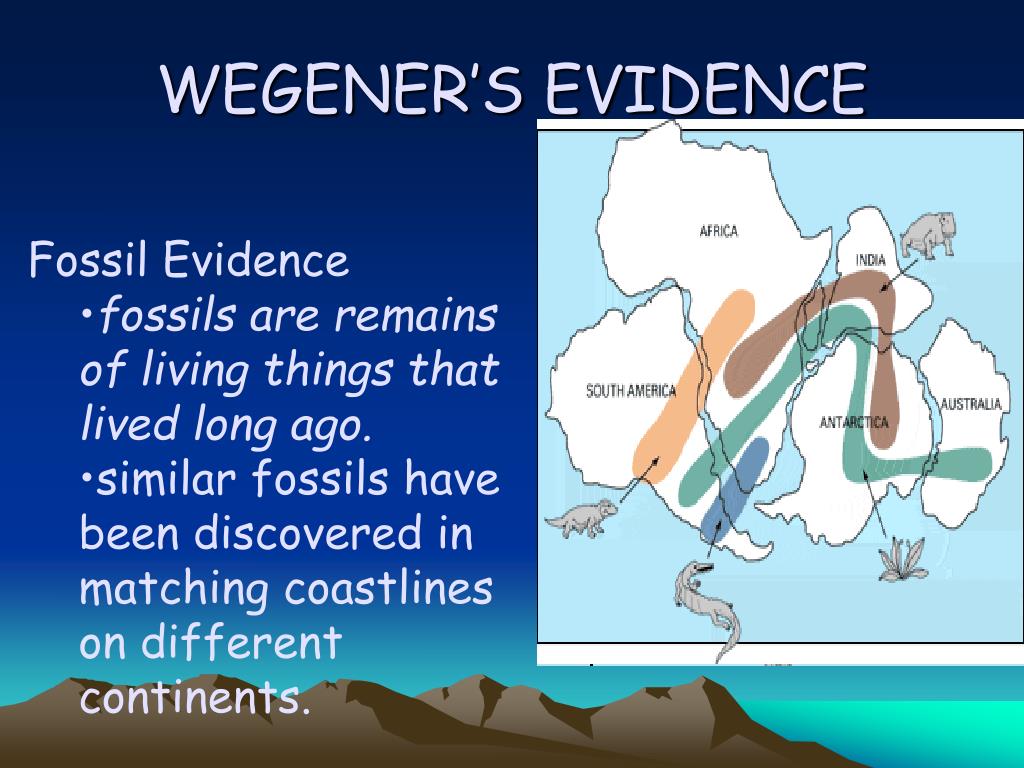
This theory of the cataclysmic origin of the Atlantic Ocean was paralleling that Note here that at the same time there was a very popular theory that the moon hadīeen formed by being ripped loose from the Pacific Ocean leaving the huge gap, and That the Atlantic Ocean might have been formed by some cataclysmic event. There was even a theory in the late 1800s Very soon after that, there were suggestions that there had been a huge continent, It was noticed first by Francis Bacon back in early 1500s. Well, the shape of the continents was noted almost as soon as maps Is it just a coincidence that the continentsįit together so well, and that the distribution of a particular animal happens to Which was a not particularly noteworthy reptile, which was found only on these two The black line that runs through the center of the two continents represents theĭistribution of a particular type of fossil called "Mesosauras," In fact, if I move SouthĪmerica and Africa back together, I see that they fit together almost perfectly. Ocean fit together so well, almost like a jigsaw puzzle. It's curious that the continents on opposite sides of the Atlantic In fact, plate tectonics actually combine two other theories, continentalĭrift and seafloor spreading into a comprehensive global theory. Of fossil and living organisms on the continents. It also helps us understand the youthful age of the sea floor and the unusual distribution On the continents, and even, in fact, describes the shapes and locations of the continents.
It explains mountain building and rock deformation Plate tectonics is a unifying theory, whichĮxplains many features and processes that we find on the Earth. Is spherical, and, also, the realization that the Earth is like another planet and Great that it may turn out be be equal in magnitude to the realization that the Earth For more about his extremely important contributions to Earth science, visit the NASA website to see a collection of articles on Alfred Wegener.THE BIRTH OF A THEORY Plate tectonics is a revolution in Earth Science, a revolution so However, within a few decades that was all to change. At the time of his death, his ideas were tentatively accepted by only a small minority of geologists, and soundly rejected by most. It was quickly shown that these forces were far too weak to move continents, and without any reasonable mechanism to make it work, Wegener’s theory was quickly dismissed by most geologists of the day.Īlfred Wegener died in Greenland in 1930 while carrying out studies related to glaciation and climate. Wegener proposed that the continents were like icebergs floating on the heavier SIMA crust, but the only forces that he could invoke to propel continents around were poleflucht, the effect of Earth’s rotation pushing objects toward the equator, and the lunar and solar tidal forces, which tend to push objects toward the west. It was understood by this time that the continents were primarily composed of sialic material ( SIAL: silicon and aluminum dominated, similar to “felsic”), and that the ocean floors were primarily simatic ( SIMA: silicon and magnesium dominated, similar to “mafic”). In fact the continental fits were not perfect and the geological matchups were not always consistent, but the most serious problem of all was that Wegener could not conceive of a credible mechanism for moving the continents around. It was translated into French, English, Spanish, and Russian in 1924. He revised this book several times up to 1929. Wegener first published his ideas in 1912 in a short book called Die Entstehung der Kontinente ( The Origin of Continents), and then in 1915 in Die Entstehung der Kontinente und Ozeane ( The Origin of Continents and Oceans). \) The distribution of the Carboniferous and Permian Karoo Glaciation (outlined in blue).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
